py速成学习
[TOC]
python
使用print
hello world
1
print("hello world")值得注意的是使用py的打印函数是
printf并没有fpy是一门脚本语言所以我们写一句话也是可以运行出结果的
字符串怕拼接
1
print("hello"+" world")换行和打印多行
1
2
3
4print("""床前明月光,
疑是地上霜。
举头望明月,
低头思故乡。""")这个是和c不同的
赋值和创建一个变量
1 | |
1 | |
运算符知识
基本和C语言一致
不同或补充
**乘方符号1
2**3 # 2的3次方
导入库
使用
import1
2
3# 例如
import math
# 导入math的库,这个库是与数学计算有关的库1
2from math import sin
# 从math中导入sin
基础数据类型
字符串
基本和c++一样
len求字符串长度
[]使用索引得到字符
浮点型只有
float布尔类型
必须是大写开始
TrueFalse使用type()打印当前变量的类型
获取用户的输入
使用
input1
2int_num=int(input("请输入一个整数:"))
print(int_num)使用input读取用户的输入是一个string,所以我们使用int()函数转换成int才是我们需要的Int_num
同样的转换函数还有很多比如
float等都是将
判断语句
1 | |
逻辑运算
与C语言不一样
and与 ==&or或 ==|not非 ==!
所谓的不同都是符号发生了变化,本质并没有很大的变化
列表
列表是可变的
创建和使用列表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14# 列表
list=["信安","实验班","物理网","网工"]
print(list)
# 添加元素
list.append("网安")
print(list)
# 删除元素
list.remove("网安")
print(list)
# 求长度
print(len(list))
# 通过索引得到元素
print(list[1])
键值对的使用
1 | |
循环
for1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36# 键值对和元组的使用
# 普通的键值对
key_value1={"chg":1,
"zjy":2,
"test":3}
print(key_value1["chg"])
print(len(key_value1))# 有几个键值对
key_value1["test2"]=4 # 添加键值对
print(key_value1["test2"])
# 判断是否存在
if "xxxx" in key_value1:
print(key_value1["chg"])
else:
print("don't hava")
# 使用循环打印键值对
for name in key_value1.keys(): # .key()方法是读取出所有的key。还有/value是读取所有值。使用.item是读取所有的键值对
print(name)
for key_value in key_value1.items():#读取出来是一个元组
print(key_value)
for num in key_value1.values():
print(num)
total = 0
for i in range(0,101): # 范围是0~100,括号左边的取不到 range()还有第三个参数表示步长
total+=i
print(total)
while()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9is_true=True
i=0
while is_true:
i+=1
if i==100 :
is_true=False
print(i)
格式化字符串
1 | |
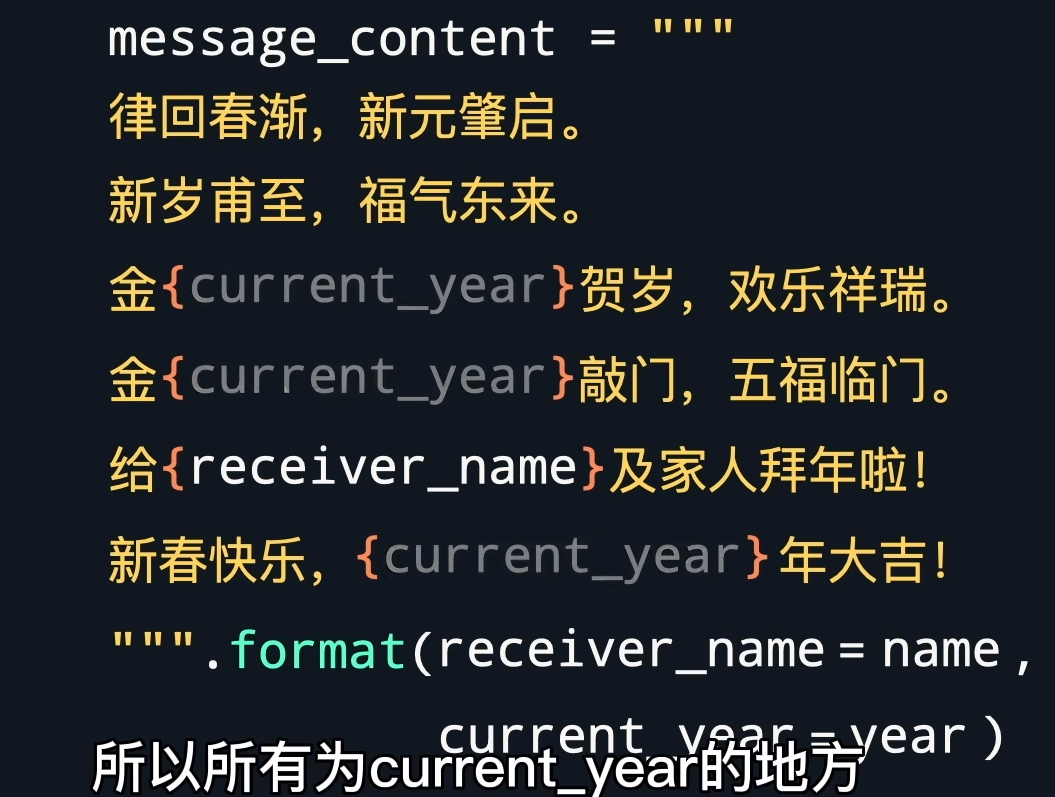
定义函数
1 | |
导入第三方库
- 通过
pypi.org网站查看库 - 通过
pip install 仓库名安装 - 使用
import引入
面向对象
使用对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class Student:
def __init__(self,id,name):
self.id=id
self.name=name
self.grades={"语文":0,
"数学":1,
"英语":2}
def set_grades(self,course,grade):
if course in self.grades:
self.grades[course]=grade
def print_grades(self):
for course in self.grades:
print(f"{course}的成绩是{self.grades[course]}")
chg=Student("10010","chg")
print(chg.id)
print(chg.grades)
chg.set_grades("数学",122)
print(chg.grades)
chg.print_grades()继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37class Student:
def __init__(self,id,name):
self.id=id
self.name=name
self.grades={"语文":0,
"数学":1,
"英语":2}
def set_grades(self,course,grade):
if course in self.grades:
self.grades[course]=grade
def print_grades(self):
for course in self.grades:
print(f"{course}的成绩是{self.grades[course]}")
def do_homework(self):
print("做作业")
class Pupils(Student):
def __init__(self,id,name,other_subjects):
super().__init__(id,name)# 调用构造函数
self.other_subjects=other_subjects
chg=Student("10010","chg")
print(chg.id)
print(chg.grades)
chg.set_grades("数学",122)
print(chg.grades)
chg.print_grades()
# 创建子类
test_student=Pupils(244,"test_student","C语言")
print(test_student.other_subjects)
文件
文件读取的模式有一下几种

读文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26file=open("C:\\Users\\12414\\Desktop\\test.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
print(file.readline())# 读一行
print(file.read(10))
file.seek(0)
# 使用while读取文本
str=file.readline()
while str!="":
print(str)
str=file.readline()
# 使用列表
file.seek(0)
lines=file.readlines()
for line in lines:
print(line)
file.close()
with open("C:\\Users\\12414\\Desktop\\test.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as file:# 执行完后会自动关闭
print(file.readline())
写文件
1
2
3
4with open("C:\\Users\\12414\\Desktop\\test.txt","w",encoding="utf-8") as file:# 遍历
file.write("this a string")
py速成学习
https://tsy244.github.io/2023/07/13/python/py基础学习/