栈和队列
[TOC]
栈和队列
栈定义和特点

- 栈:先进后出
- 队列:先进先出(排队的问题)
顺序栈的表示和操作实现
- 约定
an端为栈顶,a1端为栈底
操作
初始化 制造一个空栈
InitStack(&S)销毁栈
DestroyStack(&S)判断是否为空
StackEmpty(S)求栈的长度
StackLength(S)取栈顶的元素
GetTop(S,&e)栈的置空操作
ClearStack(&S)入栈操作
Push(&S,e)出栈操作
Pop(&S,&e)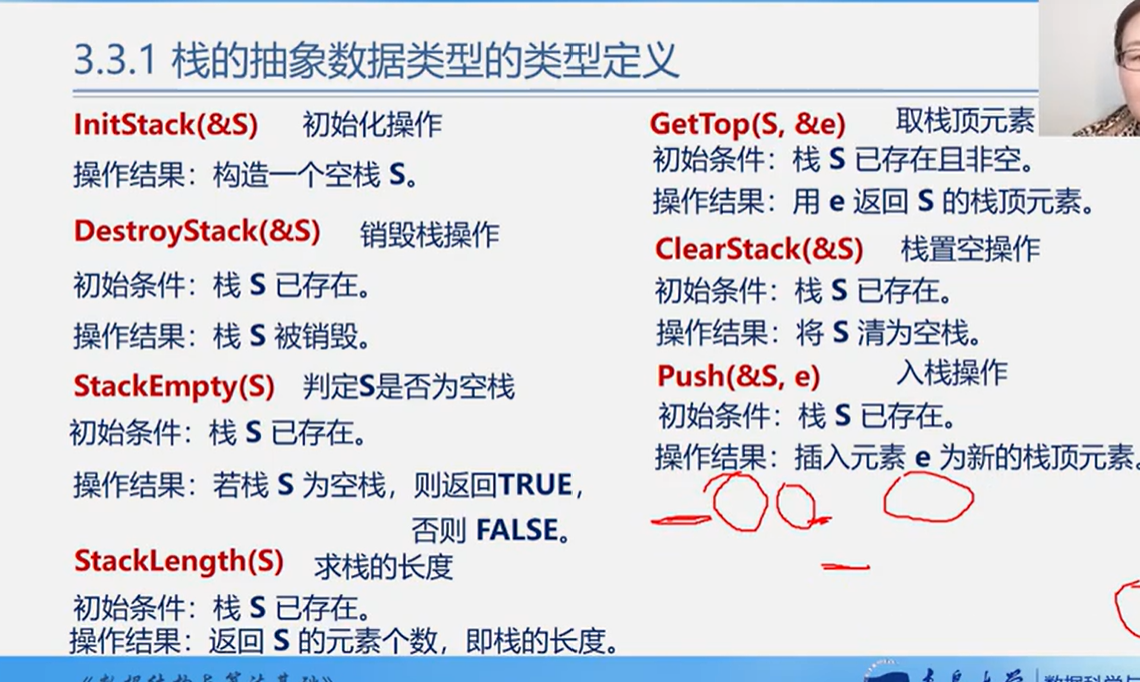
实现
两个指针,一个
top指向的是真正的栈顶的上面一个指针,一个base指向的是栈底的地址空栈的标志
top和base都指向的是0栈满的标志
top-base==stacksize
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define status int
#define OK 1
#define ERROR (-1)
#define true 1
#define false 0
#define ElemType int
#define MAXSIZE 50
#define OVERFLOW (-1)
typedef struct SqStack{
ElemType* base;
ElemType* top;
int stackSize;
}SqStack;
status destroyStack(SqStack* sqStack){
if(sqStack->base==NULL){
return ERROR;
}
free(sqStack->base);
sqStack->stackSize=0;
return OK;
}
status initStack(SqStack* sqStack){
if(sqStack==NULL){
return ERROR;
}
sqStack->base=(ElemType*)malloc(sizeof (ElemType)*MAXSIZE);
if(sqStack->base==NULL){
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
sqStack->top=sqStack->base;
sqStack->stackSize=MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
status StackEmpty(SqStack sqStack){
if(sqStack.base==sqStack.top){
return true;
}
return false;
}
int StackLength(SqStack sqStack){
if(sqStack.base==NULL){
return ERROR;
}
return sqStack.top-sqStack.base;
}
status GetTop(SqStack sqStack,ElemType* e){
if(sqStack.base==0){
return ERROR;
}
*e=*sqStack.top;
return OK;
}
status ClearStack(SqStack* sqStack){
if(sqStack->base==NULL){
return ERROR;
}
sqStack->base=sqStack->top;
return OK;
}
status Push(SqStack* sqStack,ElemType e){
if(sqStack->base==NULL||sqStack->top-sqStack->base==sqStack->stackSize){
return ERROR;
}
*sqStack->top++=e;
return OK;
}
status Pop(SqStack* sqStack,ElemType* e){
if(sqStack->base==NULL|| sqStack->base==sqStack->top){
return ERROR;
}
*e=*--sqStack->top;
return OK;
}
status CreatSqStack(SqStack* sqStack){
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
Push(sqStack,i+20);
}
}
status printfStack(SqStack* sqStack){
if(*sqStack->base==NULL){
return ERROR;
}
int tem;
while(StackLength(*sqStack)>0){
Pop(sqStack,&tem);
printf("%d ", tem);
}
return OK;
}
int main()
{
SqStack sqStack;
sqStack.base=NULL;
initStack(&sqStack);
CreatSqStack(&sqStack);
printfStack(&sqStack);
destroyStack(&sqStack);
return 0;
}
栈链的表示和实现
1 | |
栈与递归
主调函数和被调函数
如:
main函数就是主调函数,在里面调用的函数被称为被调函数函数的嵌套调用的方式

队列的表示和操作原理
- 只能在表尾经行插入操作,在表头进行删除操作的线性表
- 先进先出的线性表
- 有顺序结构和链式结构(常用的是顺序结构)
队列的相关操作

队列的顺序表示和实现

对空的表示
front=rear=0队列的特殊情况

假溢出和真溢出
假溢出
rear!=0rear=MAXQSIZE但是队列中还有空余的存储空间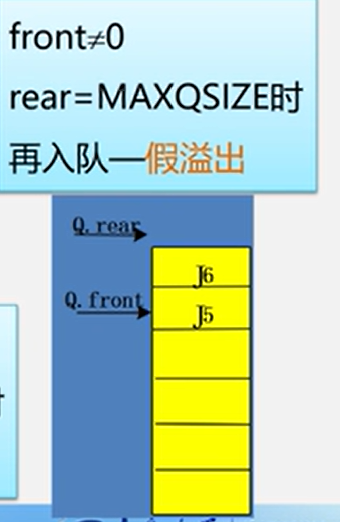
真溢出
rear=0fear=MAXQSIZE
循环队列的处理逻辑
使用
%运算,将数组变成循环但是用循环队列的是时候,我们面对的是对空和对满是一种判断条件,所以我们使用标志经行判断
一下提出三种解决办法

头文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
#include<iostream>
#define OVERFLOW (-1)
using ElemType=int;
using status=int;
const int ERROR=-1;
const int MAXSIZE=10;
class Que{
private:
ElemType* base;
int front;//地址更小的指针
int rear;//地址更大的指针
public:
Que();
~Que();
status ClearQueue();
int QueueLength();
bool GetHead(ElemType& e);
bool EnQueue(ElemType e);
bool DeQueue(ElemType &e);
};类的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
Que::Que() {
base= nullptr;
base=new ElemType [MAXSIZE];
if(base== nullptr){
std::cout<<"base new ERROR"<<std::endl;
return;
}
front=0;
rear=0;
}
Que::~Que() {
delete[] base;
front=0;
rear=0;
}
/*
Que::status Que::ClearQueue() {
return 0;
}*/
//这个算法需要想清楚
int Que::QueueLength() {
return (rear-front+MAXSIZE)%MAXSIZE;
}
bool Que::GetHead(ElemType &e) {
if(rear==front){
return false;
}
e=*(base+front);
return true;
}
bool Que::EnQueue(ElemType e) {
if((rear+1)%MAXSIZE==front){
return false;
}
*(base+rear)=e;
rear=(rear+1)%MAXSIZE;
return true;
}
bool Que::DeQueue(ElemType &e) {
if(rear==front){
return false;
}
e=*(base+front);
front=(front+1)%MAXSIZE;
return true;
}main.cpp1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
#include "myClass.hpp"
void creatQ(Que &que) {
for (int i = 0; i < MAXSIZE; ++i) {
que.EnQueue(i + 10);
}
}
void printQueue(Que &que) {
int e;
while (que.GetHead(e)) {
std::cout <<"Get: "<< e << std::endl;
que.DeQueue(e);
std::cout<<"delete: "<<e<<std::endl;
}
}
int main() {
Que queue;
ElemType elemType = 0;
int e;
queue.EnQueue(244);
std::cout << queue.QueueLength() << std::endl;
std::cout << queue.GetHead(e) << std::endl;
std::cout << e << std::endl;
creatQ(queue);
std::cout << queue.QueueLength() << std::endl;
printQueue(queue);
std::cout << queue.DeQueue(elemType) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
队列链式实现
节点的实现
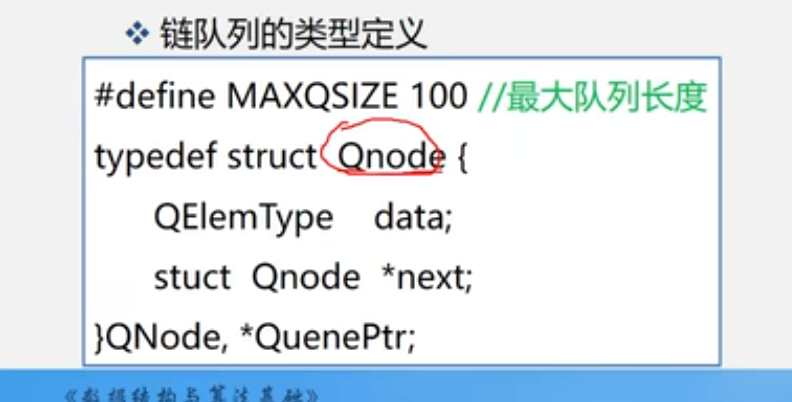
基本定义
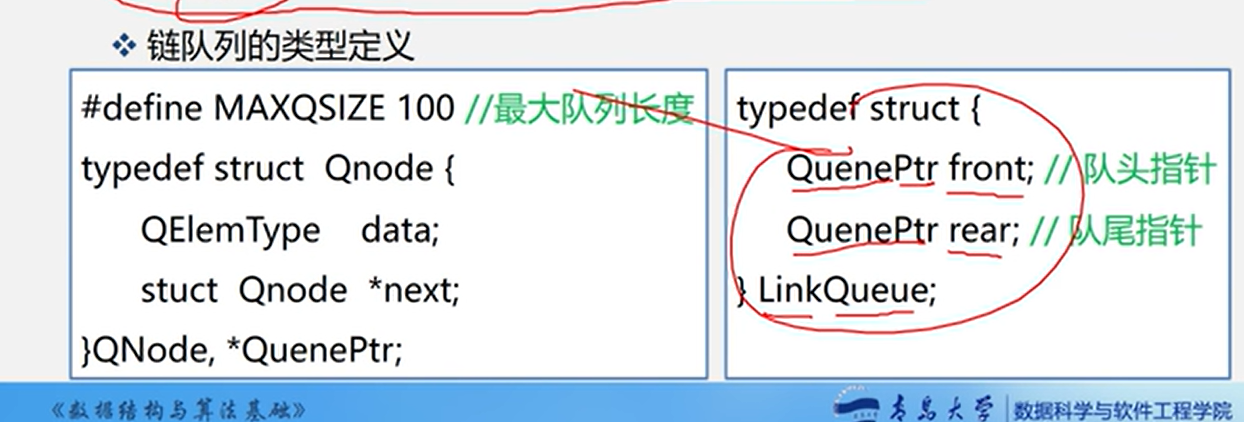
代码实例(注意win上面竟然过不了)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#define status int
#define OK 1
#define ERROR (-1)
#define true 1
#define false 0
#define ElemType int
#define MAXSIZE 10
#define OVERFLOW (-1)
typedef struct QNode {
ElemType data;
struct QNode *next;
} QNode, *QueuePtr;
typedef struct LinkQueue {
QueuePtr rear;
QueuePtr front;
} LinkQueue, *LinkQNode;
status InitNode(LinkQNode *linkQueue) {
QueuePtr queuePtr = (QNode *) malloc(sizeof(QNode));
queuePtr->next = NULL;
queuePtr->data = 0;
(*linkQueue)->front = queuePtr;
(*linkQueue)->rear = queuePtr;
}
status DestroyNode(LinkQNode *linkQueue) {
if (*linkQueue == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
QNode *deleteNode = (*linkQueue)->front;
int num = 0;
while (deleteNode != NULL) {
(*linkQueue)->front = (*linkQueue)->front->next;
free(deleteNode);
deleteNode = NULL;
deleteNode = (*linkQueue)->front;
num++;
}
(*linkQueue)->rear = NULL;
free(*linkQueue);
(*linkQueue)=NULL;
printf("%d\n", num);
return OK;
}
status CreatLinkQueue(LinkQNode *linkQueue) {
(*linkQueue) = (LinkQueue *) malloc(sizeof(linkQueue));
if ((*linkQueue) == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
(*linkQueue)->front = NULL;
(*linkQueue)->rear = NULL;
return OK;
}
status GetHead(LinkQNode *linkQNode, ElemType *e) {
*e = (*linkQNode)->front->next->data;
return OK;
}
status EnQueue(LinkQNode *linkQNode, ElemType e) {
QNode *qNode = (QNode *) malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (qNode == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
qNode->data = e;
qNode->next = NULL;
if ((*linkQNode)->front == (*linkQNode)->rear) {
(*linkQNode)->front->next = qNode;
}
(*linkQNode)->rear->next = qNode;
(*linkQNode)->rear = qNode;
return OK;
}
status DeQueue(LinkQNode *linkQNode, ElemType *e) {
if ((*linkQNode) == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
QNode *qNode;
*e = (*linkQNode)->front->next->data;
qNode = (*linkQNode)->front->next;
(*linkQNode)->front->next = (*linkQNode)->front->next->next;
free(qNode);
}
int main() {
LinkQNode linkQNode;
ElemType e;
CreatLinkQueue(&linkQNode);
InitNode(&linkQNode);
EnQueue(&linkQNode, 1);
EnQueue(&linkQNode, 244);
GetHead(&linkQNode, &e);
printf("%d\n", e);
DeQueue(&linkQNode, &e);
printf("%d\n", e);
GetHead(&linkQNode, &e);
printf("%d\n", e);
DestroyNode(&linkQNode);
return 0;
}
栈和队列
https://tsy244.github.io/2023/03/29/算法/数据结构/栈和队列/